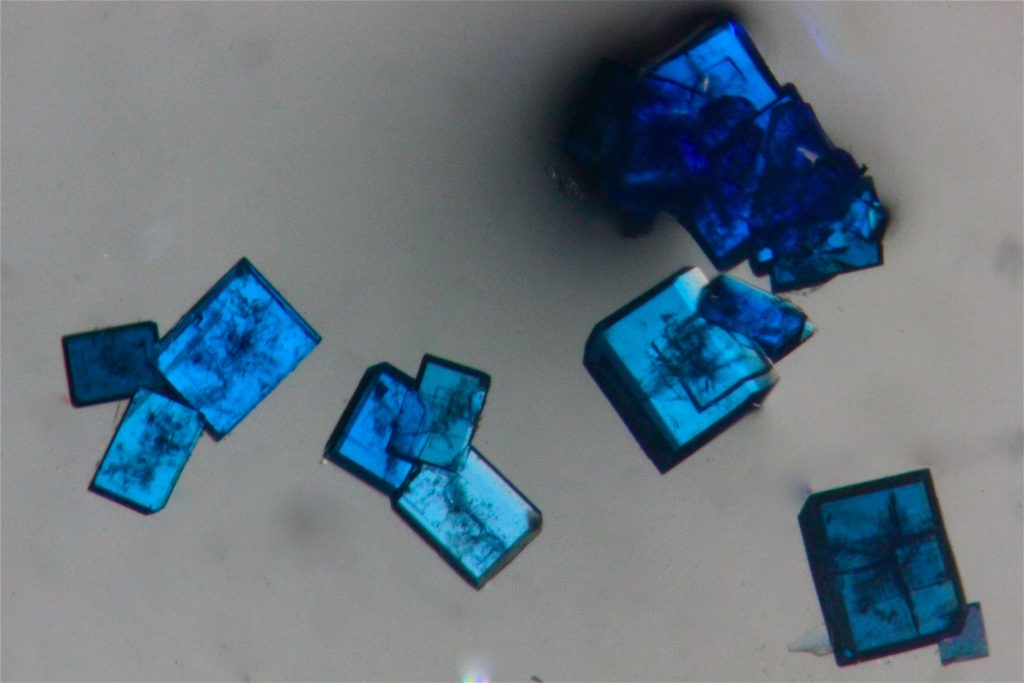
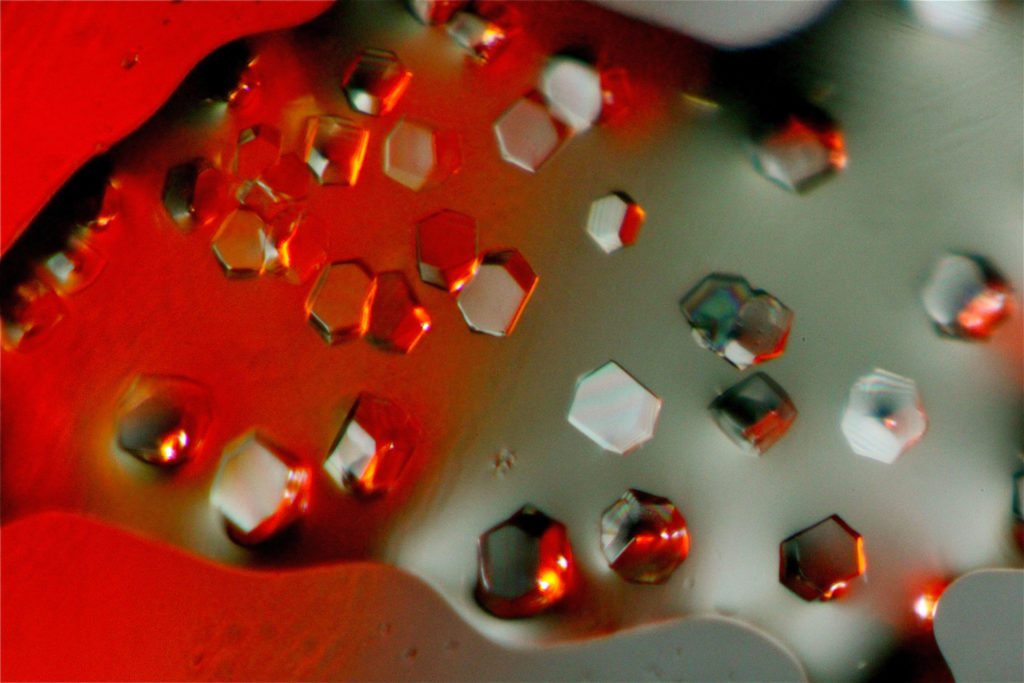
Presentation of the technique
Single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) is the reference technique in structural crystallography. Knowledge of molecular and crystalline structure is essential to understand everything relating to molecule stereochemistry (chirality, stereoisomerism, etc.), and in a more general way, structure-activity relationships. This essential information is often difficult to obtain with other methods of characterization.
In many fields, X-ray diffraction is one of the most important analytical method: catalysis, chemical reactivity, coordination chemistry, supramolecular chemistry, development of new materials, solid-state physico-chemistry, etc.
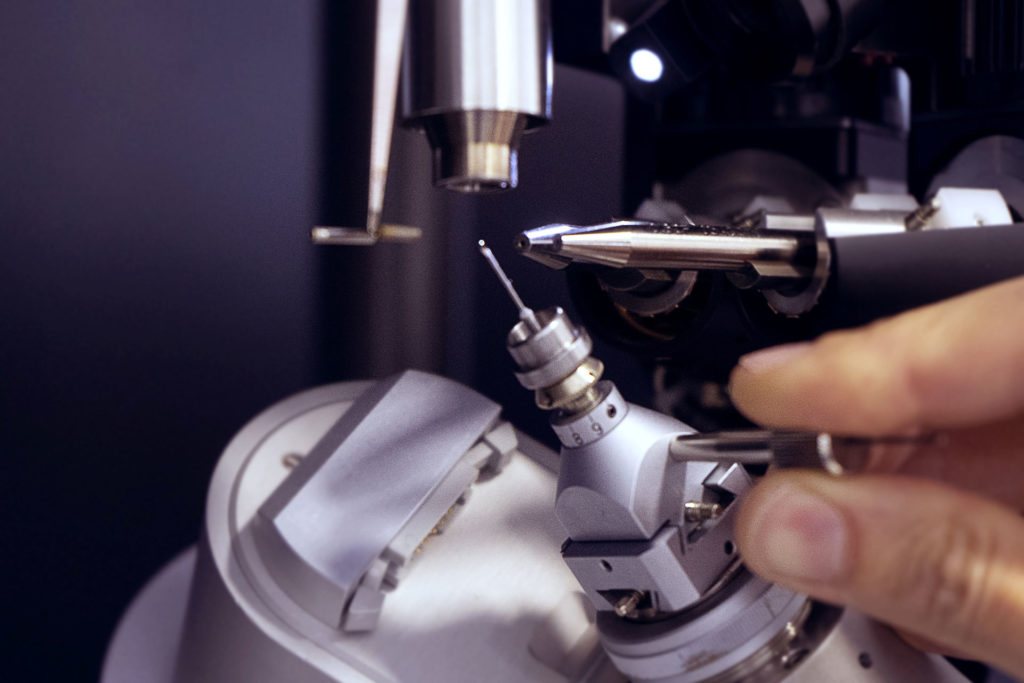
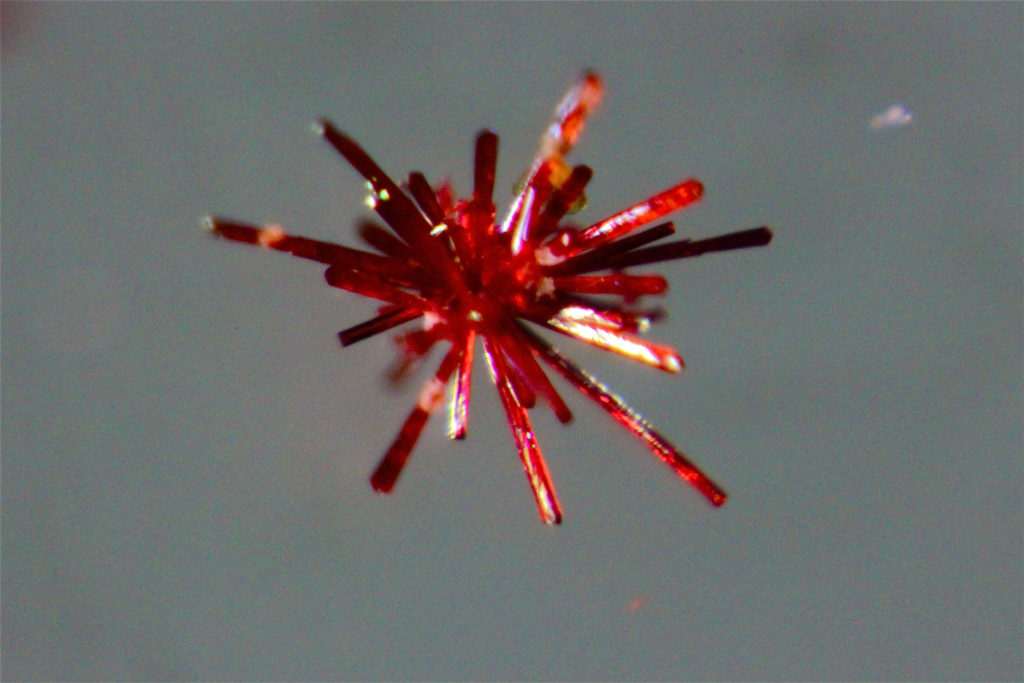
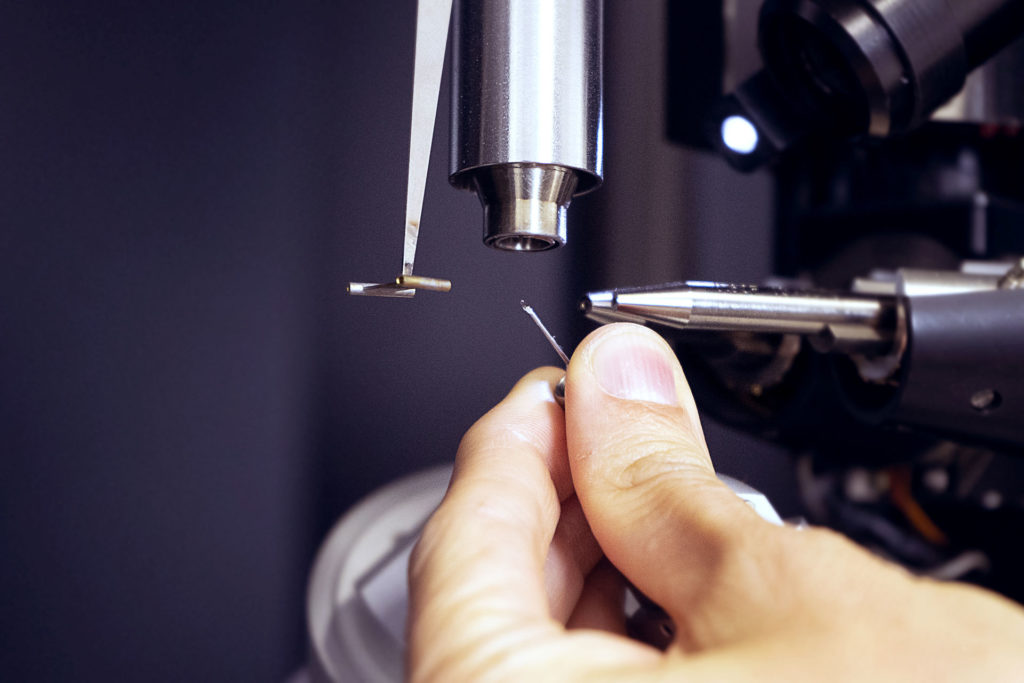
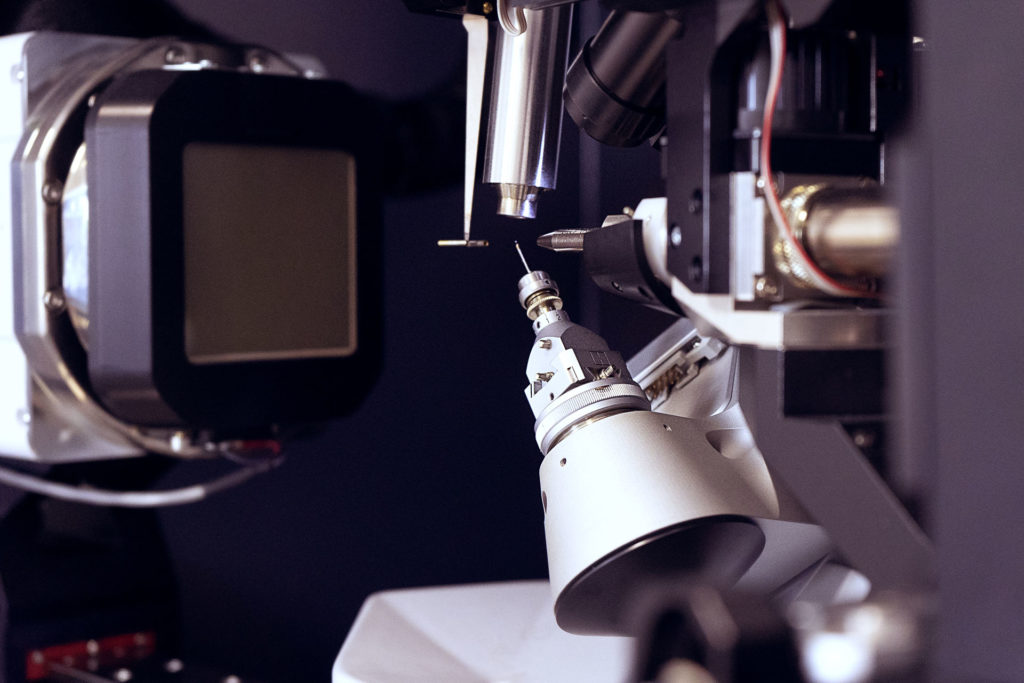
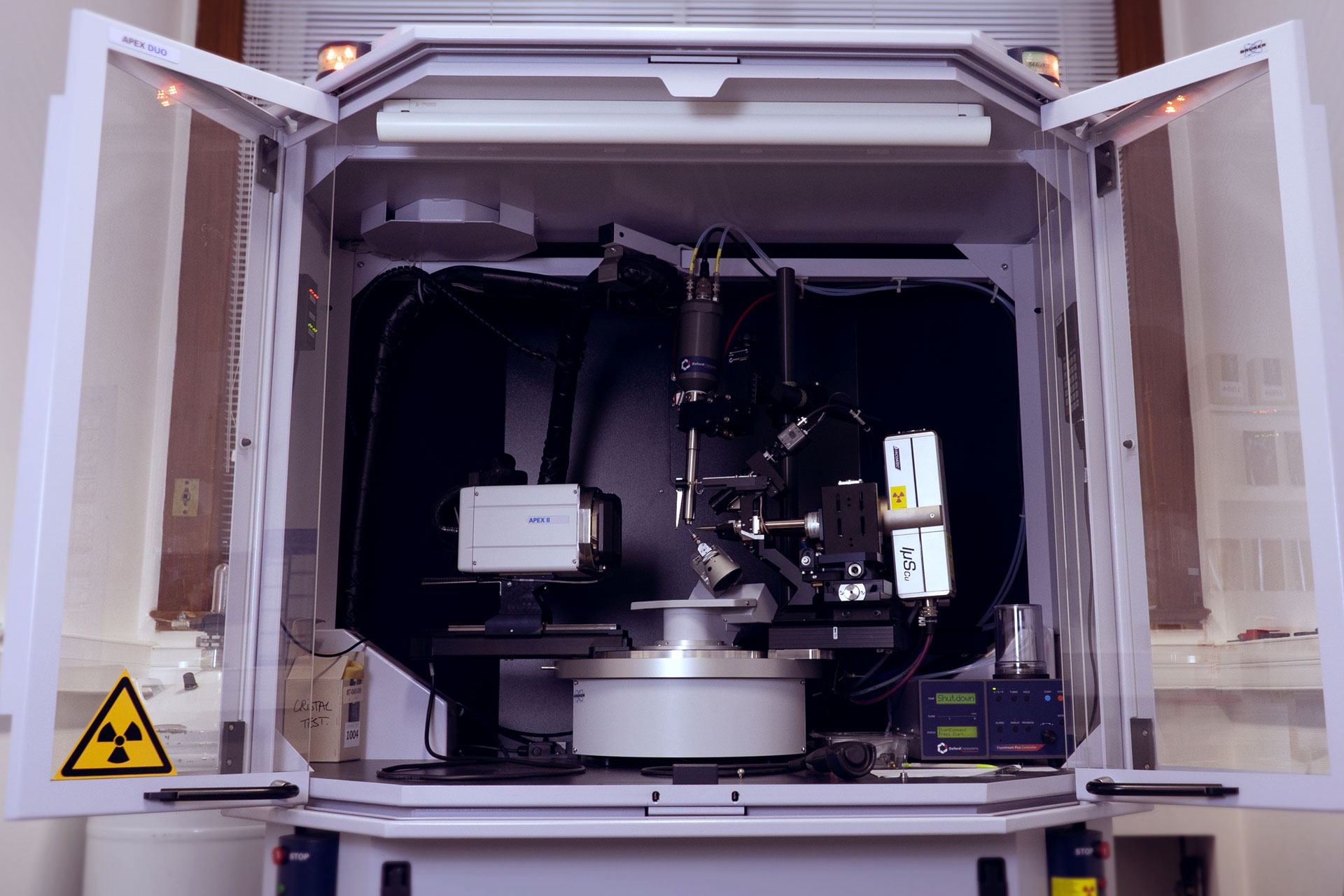
This technique is based on recording diffracted intensities by a single crystal exposed to X-ray radiation. These information are used to determine the three-dimensional structure of molecules down to atomic resolution. We have access to crystallographic and structural information on compounds: 3D atoms positions, interatomic distances and angles, intra and intermolecular bonds, molecular association modes. In advanced studies: determination of absolute configuration of molecules, charges of atoms, etc.
Service provision
All users are requested to mention in their work and publications the origin of documents due to work of DRX service of CESAMO. They also are requested to provide the service with title and full bibliographic references of the publications.
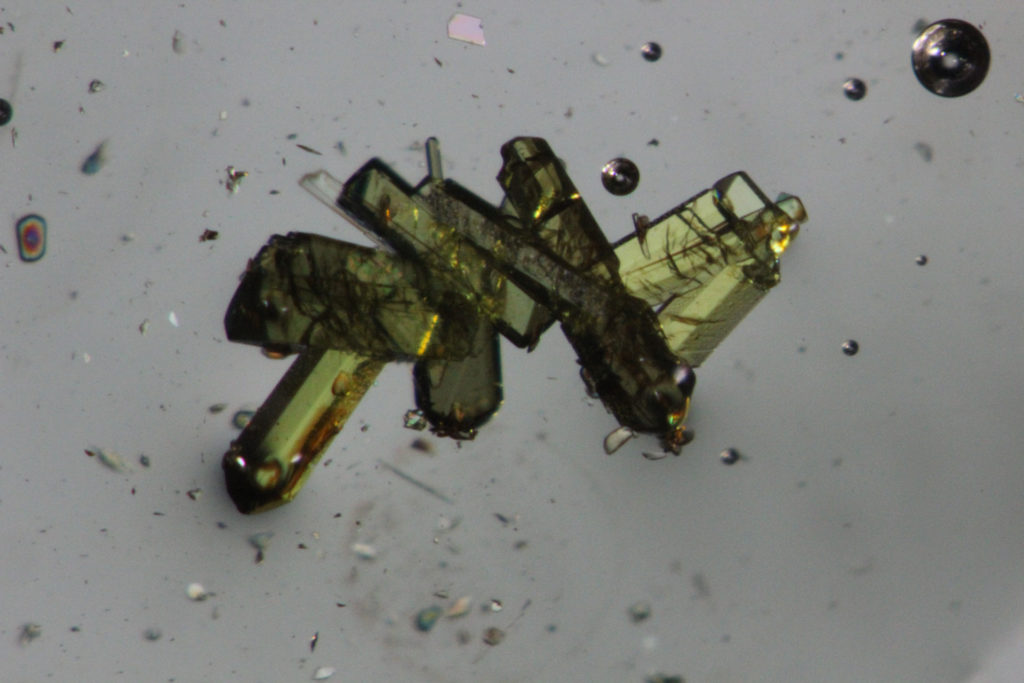
Service scope extends over small organic molecules (a few atoms) to organic, organometallic, inorganic macromolecular complexes, incliding several hundred atoms. The service takes care of all steps to determine crystal structures:-choice and assembly of the crystal,-determination of the crystalline lattice and Bravais lattice,-optimized recording of diffracted intensities and data processing,-resolution and refinement of structures,- sending of the crystallographic data file in standard .cif format, (deposit of CIF files to the structural database (CCDC) on request.)
… As well as any possible additional service required.If you have any questions: prices… Please contact
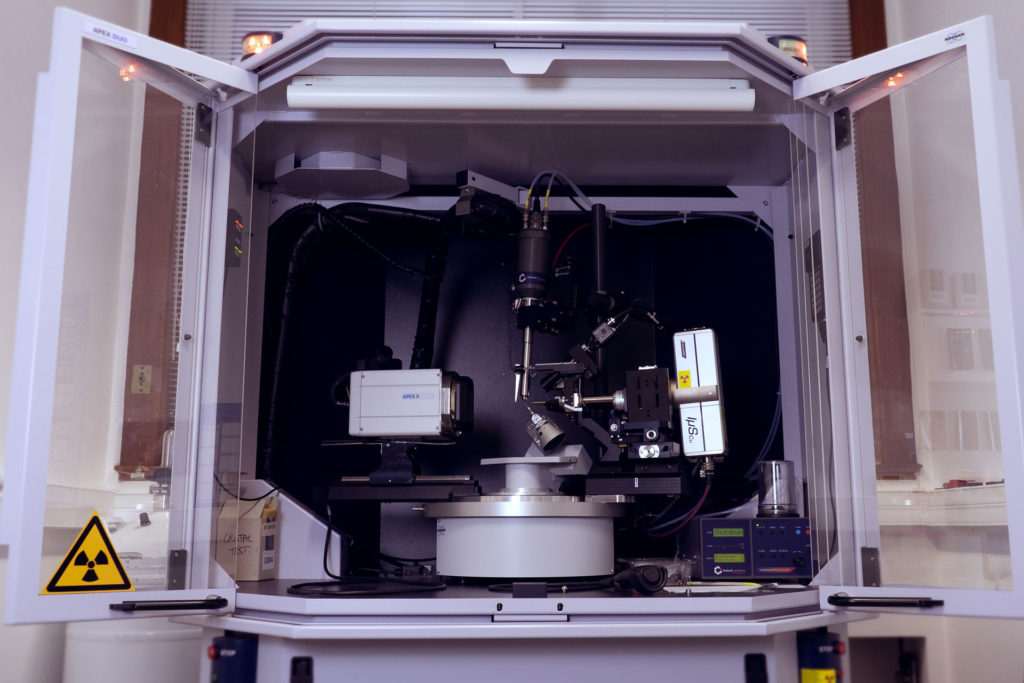
Devices
Leica M 125
XRDContacts
Aline LACOUDRE
2ème EAST floor, 2N29 Office
Phone : 05.40.00.64.48
Email : aline.lacoudre@u-bordeaux.fr